
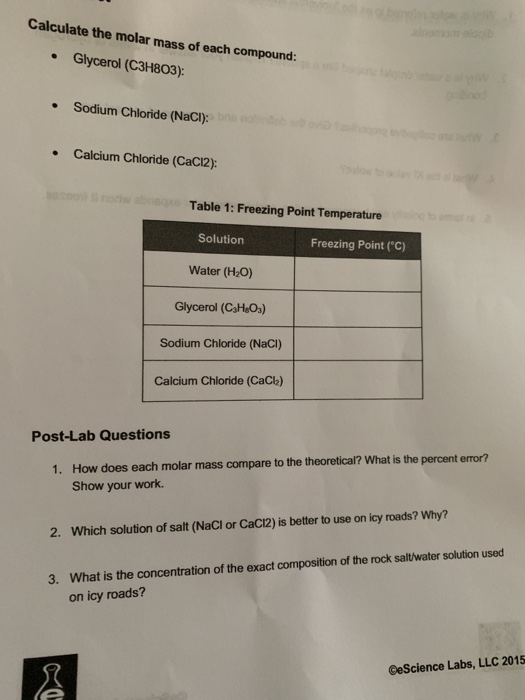
In other words, empirical refers to something that can be observed and assessed. In a glucose molecule, it represents the number of atoms of each constituent (Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen). Here is an example of a molecular formula. The numerical subscripts after the chemical symbols indicate the number of atoms.
A molecular formula also tells us the type of atom present in the molecule of a compound. In a molecule, we can find out the exact number of atoms of each element present by using a molecular formula, also known as a true formula. Chemical Formulas or Chemistry Formulas TypesĬhemical Formula can be divided into 3 types Chemistry formula tables can help you understand chemistry formulas. It is done with the help of chemical elements, their symbols, and the numerical subscripts. The formulas of chemistry are known as chemical formulas.Ī chemical formula is a way through which scientists represent the chemical proportions such as the number of atoms present in a molecule or a chemical compound. In the history of mankind, all elements have received a specific name derived from chemistry studies. The branch of science dealing with the chemical and physical properties of substances in a manner that further results in the formation of new substances is known as Chemistry. What is the formula for calculating pH?.What is the formula for the ideal gas law?.
 How do you calculate the molar mass of a compound?. What is the formula for carbon dioxide?. What is the chemical formula for water?. Chemical Formulas or Chemistry Formulas Types. The end point of a potassium dichromate(VI) titration isn't as easy to see as the end point of a potassium manganate(VII) one. However, the color is made difficult by the strong green also present. This gives a violet-blue color in the presence of excess potassium dichromate(VI) solution. There are several such indicators - such as diphenylamine sulfonate. These change color in the presence of an oxidising agent. With potassium dichromate(VI) solution you have to use a separate indicator, known as a redox indicator. Unfortunately potassium dichromate(VI) solution turns green as you run it into the reaction, and there is no way you could possibly detect the color change when you have one drop of excess orange solution in a strongly colored green solution. As soon as you add as much as one drop too much, the solution becomes pink - and you know you have reached the end point. As you run the potassium manganate(VII) solution into the reaction, the solution becomes colorless. Potassium manganate(VII) titrations are self-indicating. The main disadvantage lies in the color change. That means that you don't get unwanted side reactions with the potassium dichromate(VI) soution. Potassium manganate(VII) oxidises chloride ions to chlorine potassium dichromate(VI) isn't quite a strong enough oxidising agent to do this. Potassium dichromate(VI) can be used in the presence of chloride ions (as long as the chloride ions aren't present in very high concentration). That isn't true of potassium manganate(VII). That means that it can be made up to give a stable solution of accurately known concentration. Potassium dichromate(VI) can be used as a primary standard. There are advantages and disadvantages in using potassium dichromate(VI). You will see that the chromium(III) sulfate and potassium sulfate are produced in exactly the right proportions to make the double salt.
How do you calculate the molar mass of a compound?. What is the formula for carbon dioxide?. What is the chemical formula for water?. Chemical Formulas or Chemistry Formulas Types. The end point of a potassium dichromate(VI) titration isn't as easy to see as the end point of a potassium manganate(VII) one. However, the color is made difficult by the strong green also present. This gives a violet-blue color in the presence of excess potassium dichromate(VI) solution. There are several such indicators - such as diphenylamine sulfonate. These change color in the presence of an oxidising agent. With potassium dichromate(VI) solution you have to use a separate indicator, known as a redox indicator. Unfortunately potassium dichromate(VI) solution turns green as you run it into the reaction, and there is no way you could possibly detect the color change when you have one drop of excess orange solution in a strongly colored green solution. As soon as you add as much as one drop too much, the solution becomes pink - and you know you have reached the end point. As you run the potassium manganate(VII) solution into the reaction, the solution becomes colorless. Potassium manganate(VII) titrations are self-indicating. The main disadvantage lies in the color change. That means that you don't get unwanted side reactions with the potassium dichromate(VI) soution. Potassium manganate(VII) oxidises chloride ions to chlorine potassium dichromate(VI) isn't quite a strong enough oxidising agent to do this. Potassium dichromate(VI) can be used in the presence of chloride ions (as long as the chloride ions aren't present in very high concentration). That isn't true of potassium manganate(VII). That means that it can be made up to give a stable solution of accurately known concentration. Potassium dichromate(VI) can be used as a primary standard. There are advantages and disadvantages in using potassium dichromate(VI). You will see that the chromium(III) sulfate and potassium sulfate are produced in exactly the right proportions to make the double salt.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
